Port selector
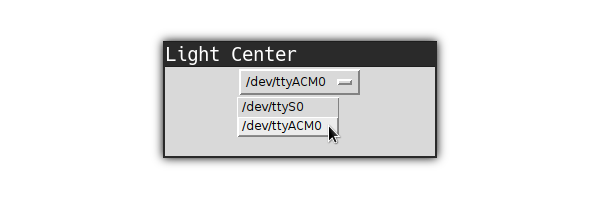
This program should provide a drop-down menu to select a serial port but some parts are missing, fix them
Once the program is fixed and you select the correct port, the LEDs on your Arduino should flash
Using object oriented programming to write better GUIs
1 class ButtonsWindow(object):
2 def __init__(self):
3 self.setup_buttons()
4
5 def run(self):
6 self.window.mainloop()
The code above contains an object oriented approach to GUI programming
but it also contains a few errors and unimplemented functionality
fix the program so that whenever a button is pressed
the corrseponding text is print()ed on the terminal
1 class PrintingButton(object):
2 def __init__(self, window, label):
3 self.label= label
4 self.button= tk.Button(
5 window, text=label,
6 command= self.on_pressed
7 )
8 self.button.pack()
9
10 def on_pressed(self):
11 print(self.label)
Download and flash the atuino Arduino sketch introduced in tutorial 16
Copy the content of the
atuino python code
into a file called atuino.py
Open a terminal, cd into the directory where
you saved the atuino.py file and type
python (on Windows) / python3 (everywhere else)
to start an interactive python session
1 >>> import atuino
2 >>> arduino= atuino.Arduino('/dev/ttyACM0')
3 >>> led= atuino.OutputPin(arduino, 13)
4 >>> led.turn_on()
5 >>> led.turn_off()
Enter the python statements above into the
interactive session, remember to replace
/dev/ttyACM0 with the actual name of your
serial port
The led.turn_on/led.turn_off statements
should turn the on-board LED on/off
Hint: You can use the Arduino IDE to find the name of your serial port

This program should provide a drop-down menu to select a serial port but some parts are missing, fix them
Once the program is fixed and you select the correct port, the LEDs on your Arduino should flash
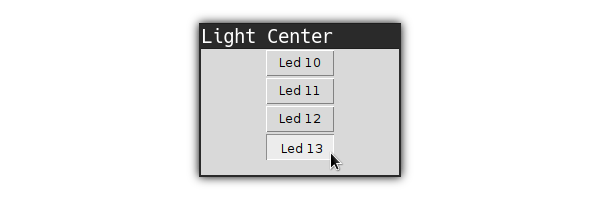
This program contains a working drop-down list and displays buttons to control the LEDs attached to the Arduino
The LED controlling part does not work, find out why and fix the problem
